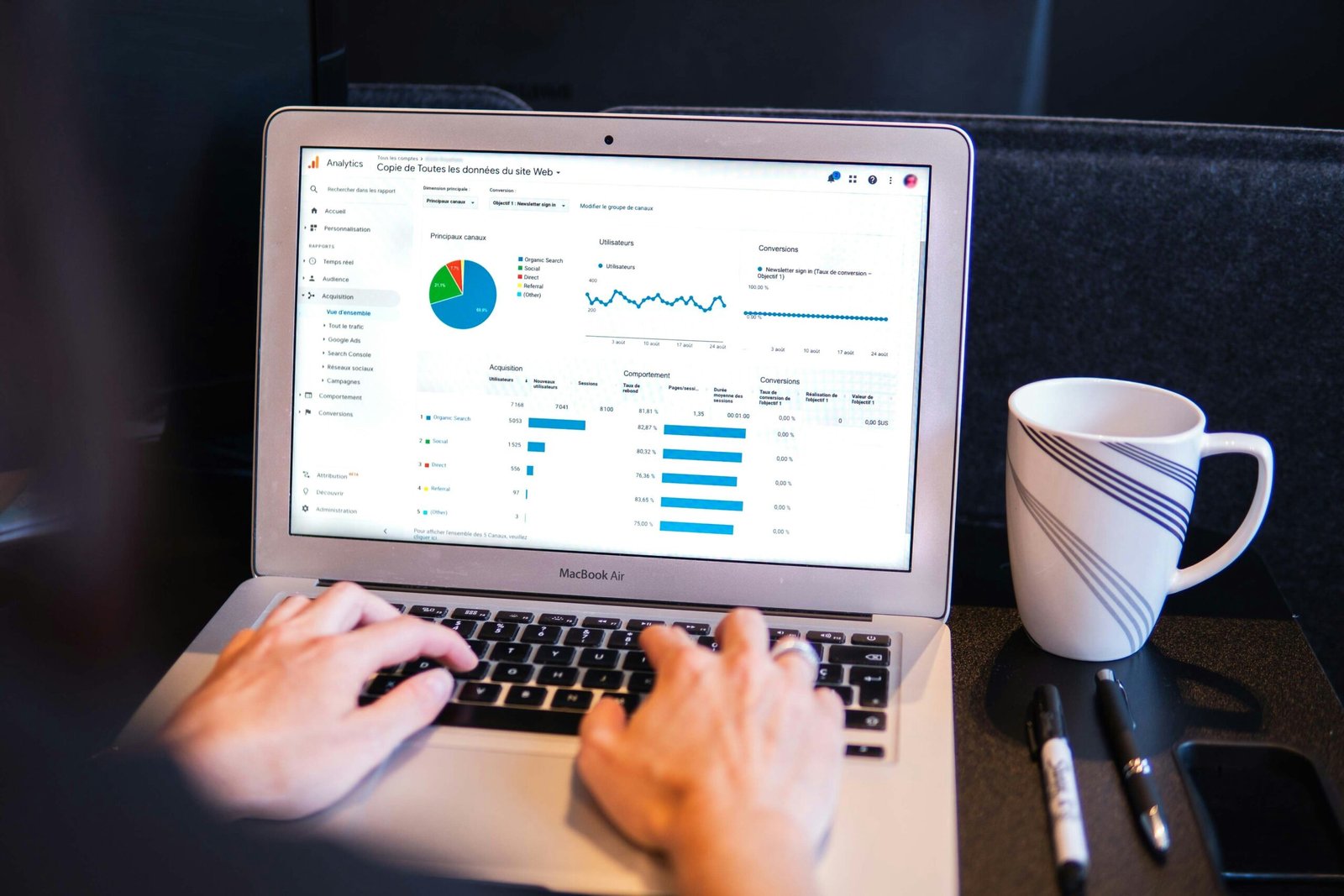
Understanding Big Data and its Importance in Economics
Big data refers to the vast volumes of structured and unstructured data that are generated at an unprecedented rate from various sources, including social media, transaction records, sensors, and more. These data sets possess characteristics such as volume, velocity, and variety, which distinguish them from traditional data sets. The enormity of big data, represented by terabytes and petabytes, allows economists to extract valuable insights that were previously unattainable. The speed at which this data is generated enables real-time analysis, making it a powerful tool in economic decision-making.
In economic contexts, big data plays a crucial role in understanding market trends and consumer behavior. By analyzing consumer data across multiple platforms, economists can identify patterns and preferences, which can inform marketing strategies and economic policies. The ability to harness the diversity of data types—from numerical data and text to images and videos—facilitates a comprehensive examination of economic phenomena. This understanding can lead to improved forecasting models that can adapt to changing consumer behaviors and market conditions.
Moreover, big data analysis presents significant benefits, particularly in optimizing resources and enhancing decision-making processes. Businesses can leverage the insights drawn from big data to refine their operational strategies and improve customer engagement. However, the interpretation of big data is not without risks. Economists and data analysts must navigate potential pitfalls, such as data bias and privacy concerns, which can lead to erroneous conclusions if not addressed properly.
Thus, recognizing the potential of big data within the economic sphere is vital for leveraging its capabilities effectively while being aware of the inherent challenges. By understanding the components and implications of big data, economists can utilize these insights to foster informed decision-making and drive economic growth.
(Purchase today by clicking on the image)
Technological Advancements Driving Big Data Analysis
The surge in technological advancements has significantly transformed the landscape of big data analysis, enabling economies to harness data in ways previously deemed impossible. One of the primary catalysts for this revolution is artificial intelligence (AI). AI algorithms process enormous amounts of data rapidly, allowing for predictive analytics that can forecast market trends with remarkable accuracy. By learning from historical data, AI systems facilitate nuanced economic decision-making, enabling policymakers and businesses to derive actionable insights that enhance operational efficiency.
Machine learning (ML) extends the capabilities of AI by utilizing statistical techniques to enable systems to learn and improve from experience. ML algorithms can automatically identify patterns and correlations within vast datasets. In economic policymaking, for instance, ML models are harnessed to assess the potential impacts of fiscal policies on various sectors, thus enabling more informed and data-driven decisions that consider numerous economic variables and scenarios.
Cloud computing serves as a foundational technology, offering scalable resources for storing and processing big data. It allows organizations to access and analyze large datasets without the constraints of physical infrastructure. By facilitating collaboration among diverse stakeholders, cloud computing enhances the accessibility of data analytics tools, ensuring that critical economic indicators can be evaluated in real-time, thus streamlining decision-making processes.
Moreover, dedicated data analytics tools are becoming integral to economic environments. These platforms visually represent complex data through interactive dashboards, simplifying the interpretation of large datasets. Their implementation in financial institutions has led to more precise economic forecasting, risk assessment, and strategic planning. Examples of successful applications abound, including the use of data-driven insights by central banks to evaluate monetary policies and their influence on inflation rates.
Overall, the convergence of AI, ML, cloud computing, and data analytics tools marks a significant leap forward, empowering economists and decision-makers to leverage big data for improved accuracy and efficiency in economic decision-making.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications of Big Data in Economic Decision-Making
The utilization of big data analysis has transformed economic decision-making across various sectors, allowing organizations and governments to derive insights that were previously unimaginable. One notable application can be found in financial markets, where predictive analytics is employed to forecast stock performance and market trends. For instance, firms like Goldman Sachs utilize algorithms that analyze millions of data points, including historical prices, trading volumes, and news sentiment, to create predictive models. This enhances their capability for risk assessment and investment strategy development, ultimately leading to improved financial outcomes.
In the retail sector, customer segmentation has become pivotal for enhancing sales and customer satisfaction. Companies such as Target leverage big data to analyze consumers’ shopping behaviors and preferences. By tracking purchase histories and online interactions, Target can identify distinct customer segments and tailor marketing campaigns accordingly. This method not only maximizes advertising effectiveness but also bolsters customer loyalty through personalized experiences, demonstrating the favorable business performance that results from informed economic decisions.
Additionally, governments have started to realize the importance of big data insights in shaping effective policies. For example, the city of New York employs big data analytics to analyze economic indicators such as unemployment rates and housing data. This information guides policymakers in adjusting economic strategies, cultivating job growth initiatives, and addressing public concerns. Nonetheless, implementing big data analysis comes with challenges, including data privacy issues and the necessity for skilled personnel. Overcoming these barriers allows for significant benefits, marking a notable shift toward data-driven governance.
Ultimately, these case studies illustrate the diverse applications of big data in economic decision-making, highlighting how organizations and governments can glean valuable insights, optimize operations, and make proactive decisions that foster growth and stability.
Challenges and Future Trends in Big Data Analysis for Economics
The integration of big data analysis into economic decision-making is not without its challenges. One significant concern is data privacy. As organizations collect vast amounts of data, including personal information, ensuring the privacy and security of this data becomes crucial. Economists and data analysts must navigate complex regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, which imposes strict guidelines on how data can be collected and used. Failure to comply can result in heavy penalties, making it essential for analysts to develop robust data governance frameworks.
Another challenge is the quality and cleanliness of data. Big data often consists of diverse datasets that can be incomplete, inconsistent, or inaccurate. Poor-quality data can lead to erroneous conclusions in economic analysis, potentially impacting policy decisions and business strategies. Therefore, investments in data cleansing processes and validation techniques are vital to ensure that the insights drawn from big data are reliable and actionable.
The need for a skilled workforce is another prominent issue. The effective analysis of big data requires not only knowledge of economics but also proficiency in data science, statistics, and advanced analytical tools. The current demand for talent in this domain often outstrips supply, leading to a skills gap that must be addressed through targeted education and training programs. As the field evolves, continuous professional development will be essential for economists and analysts to keep up with new advancements.
Looking ahead, there are several emerging trends in big data technologies that could further impact economic analysis. One of these trends is the rise of decentralized data architectures, which allow for greater data sharing and collaboration across organizations while enhancing security. Additionally, advancements in real-time data processing are enabling economists to glean insights instantaneously, enhancing the speed and quality of decision-making. By overcoming current challenges and leveraging these future trends, the potential of big data analysis in economics can be fully realized.
(Purchase today by clicking on the image)